Quick Link
Technology’s Generational Warfare: 5G against 6G
Our pursuit of connectivity that is quick, dependable, and efficient has led to a cycle of advancement in mobile technology. Every generations since the early days of analog voice (1G) to the current era of 5G has fundamentally altered how we engage and communicate with technology. Now that the 6G era has arrived, it is appropriate to revisit the subject of how this next generations of technology will build upon and transcend its most recent predecessor, 5G. The extensive analysis compares and contrasts 5G and 6G in terms of their effects on different industries, technological advancements, and society at large.
Recognizing 5G: The Present Frontier

The fifth generations of mobile network technology, or 5G, is a significant advancement above 4G. It opens up a whole new realm of applications and services by introducing a completely new dimension of speed, latency, and capacity. 5G will work across a wide range of frequencies, from sub-6 GHz all the way up to millimeter waves above 24 GHz, providing extra value to performance.
Bandwidth and Speed While 4G could only support 1 Gbps of data speed, 5G would allow for 10 Gbps. High data usage applications for this cutting edge technology include augmented reality and HD video streaming.
Lateness For interactive applications and real-time communication, latency is the decisive factor. 5G can achieve a latency of just one millisecond.
Higher Capacity 5G networks can accept many more connected devices per square kilometer to adapt to the requirements of both Iot and smart cities.
Applications of 5G
Enhanced Mobile Broadband quicker downloads and better video quality are made possible by quicker speeds and larger capacities.
IoT Connectivity: Due to its massive device compatibility, 5G will be crucial in expanding IoT applications for smart homes, smart cities, and industrial settings. Driverless Automobiles: For self-driving cars and other connected vehicles to communicate in real time, 5G latency must be low. 1.4 Difficulties and Restrictions
Infrastructure Needs Small cells are required in a very dense manner for the 5G infrastructure, which is quite costly and complex.
Problems with Coverage Despite 5G’s extremely fast speeds, its higher-frequency bands have a limited penetration and range, which could result in coverage gaps.
Security Issues There are additional security challenges that need to be resolved as a result of increased connectivity and 5G network complexity.
Greetings from the 6G Era
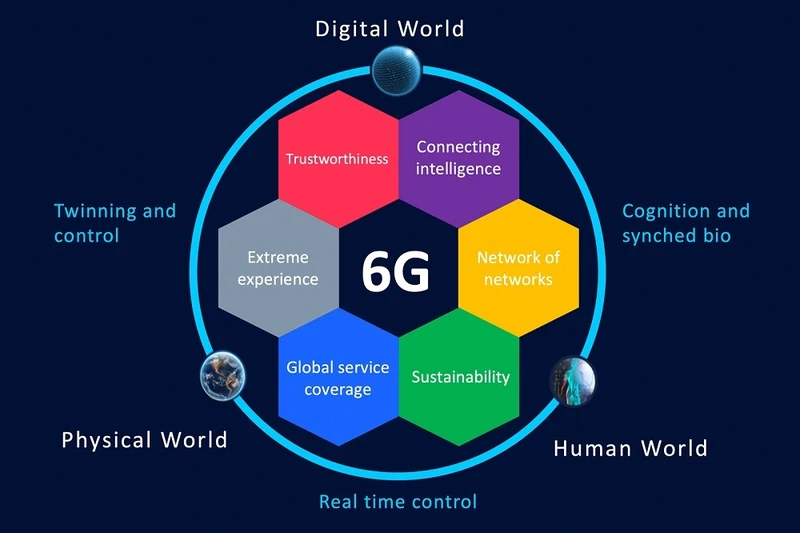
The next level of connectivity is called 6G, or sixth generations of cellular. Although it is currently in its very early phases of development, it will have advantages over 5G in terms of speed, latency, and functionality.
Ultra-High Speeds: 6G has the ability to reach data rates of roughly 100 Gbps, way generations beyond what is made feasible with 5G now. Immersion-based, ultra-high-resolution material will be made possible by it.
Extremely Low Latency 6G will be able to provide nearly instantaneous communication with latency that may perhaps drop below 1 ms, which is undoubtedly necessary for even more sophisticated applications like real-time holography.
Enhanced Trust and Assurance: greater coverage along with more dependable generations linkages, as well as some of 5G’s drawbacks.
6G Technology Enablement
Terahertz frequencies: In order to operate on 6G, a lot more bandwidth than previously possible will be required. This kind of bandwidth is only practical with very advanced technologies.
AI Integration: Performance optimization, resource management, and the implementation of intelligent applications are the three main goals of integrating AI into 6G networks.
Advanced Network Architecture: Network slicing and edge computing are two advanced network generations designs that 6G will allow, substantially increasing flexibility and efficiency. 2.4 Uses of Holographic Communications with 6G Potential: With the advent of 6G, real-time holographic communications will be possible with ultra-low latency and high speeds, revolutionizing virtual meetings and remote interactions.
Advanced AI and Robotics As a result, more complex AI applications and robotics in sectors like manufacturing, entertainment, and health will be supported by the enhanced 6G capability generations.
Finally, the full-scale implementation of smart environments—where personal gadgets and infrastructure are connected and optimized—will be made possible by 6G.
Technological ComplexityIt takes advanced network management, hardware, and software to investigate and implement 6G technology.
Allocation of Spectrum There are many obstacles to overcome in the acquisition and management of THz spectrum, including technological and regulatory difficulties.
Security and Privacy Due to greater degrees of freedom and enhanced connectivity, 6G will have privacy and security concerns similar to those faced by its predecessors.
5G vs. 6G – A Critical Evaluation
Speed and Performance
Where 5G can attain rates of 10 Gbps, 6G will fly past that to near 100 Gbps, introducing new sophisticated applications and services that weren’t conceivable at 5G speeds, such generations high-resolution VR/AR experiences.

Reactivity and Latency
Although 5G has already succeeded in achieving a low latency of about 1 millisecond, 6G aims to even lower latencies to around 1 millisecond in order to allow users to engage and communicate in almost real time with new generations.
Protection and Dependability
Because 5G is dependent on higher-frequency bands that have a shorter range of propagation, it can only provide a restricted amount of coverage. 6G just seeks to improve coverage and generational dependability by utilizing network architecture and technological advancements.
Introduced Technologies
While both 5G and 6G will leverage cutting-edge technologies, 6G will push them even farther. Among the notable advancements over 5G include the use of terahertz frequency, AI-driven network management, and sophisticated network topologies, to mention a few.
Applications and Use Cases
Whereas 5G has enabled numerous applications, ranging from smart cities to autonomous vehicles, 6G is expected to expand the opportunities. From real-time holography to fully integrated smart environments, 6G opens up endless new opportunities and possibilities of new experience types.
Security and Privacy
Security and privacy concerns are a part of both 5G and 6G. New generations vulnerabilities introduced in 5G and their fix, among others, are expected in 6G, considering its higher functionalities and a wider range of devices it will be able to connect.
The Future Outlook – What to Expect
Industry Impact
The shift from 5G to 6G will affect many verticals. In health, 6G will enable real-time remote surgery and advanced telemedicine. For manufacturing, it may ignite a revolution generations of automation and smart factories. In entertainment, 6G will spur the reinvention of content delivery with immersive experiences.
Societal Implications
As 6G technology develops, so too will how we live, work, and interact with one another. For instance, real-time holographic communications and ubiquitous connectivity could transform what we consider human interactions and civic participation.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Implementation of 6G will need to be thoughtful regarding regulatory and ethical considerations. In moving forward toward this next generations of connectivity, a balance has to be struck between innovation, privacy, security, and equitable access.
Preparing for the Future
Businesses, governments, and individuals should start preparing for the era of 6G, based on how technological development relates to investment in research and infrastructure and also needed challenges in advance.
Last Words of Wisdom
There is a significant generations difference between 5G and 6G; 5G has really paved the way for improvements in speed, capacity, and connectivity, while 6G is expected to push these developments even farther with its significantly higher performance, capabilities, and applications. Moving into the 6G era, the prospects for innovation and transformation will be huge—plausibly changing both the future of technology and society.
This way, we know what the difference from 5G to 6G is and what each stepvolution means and can face the future with open arms. Be it chances in improved connectivity, in innovative application, or in interfacing with technologies; the future is going to be an exhilarating expanse of possibles.
For more content like this visit for online earning blogs visit autoearn or visit our Fcaebook page.


